When customers shop online, paying for the product or service completes the buyer’s journey for them. When integrated with an online business website, a payment gateway provides a secure and convenient channel to facilitate the payment process. A successful payment process completed in a secure environment will influence a customer’s decision to make a purchase, driving up sales for the eCommerce business. Increased sales make payment gateways an integral part of eCommerce website development.
Payment Gateways have evolved over the last few years to offer increased security and functionalities. For a startup, it may get confusing to choose between the multiple payment gateway service providers in the market. In this blog, read all about payment gateways that will help to discern through the list of top payment gateways for your eCommerce marketplace.
What Are Payment Gateways?
Payment gateways are simply gateways that let the customer pay online. The customers get to complete the payment transaction from a page within the eCommerce website they are using.
It is a service that connects the website to the bank to complete the transaction. Although the service can be used by any website that requires an online transaction, they are integral to eCommerce websites.
Payment gateways are one of the most important eCommerce development solutions. They have benefitted the eCommerce industry immensely by allowing digital transactions in a secure environment. This has helped in garnering the customers’ trust for eCommerce websites.
See Also: eCommerce International Shipping Best Practices
Top 7 Payment Gateways for Online Businesses (eCommerce) in 2021:
1. Square

Square is a payment gateway by Square, INC. It is known for affordability and user-friendly payment processing. The payment gateway focuses on simplicity, which makes it an ideal choice for a startup. Square offers a centralized UX with access to most features from the dashboard itself.
Square offers chargeback protection, fraud detection, account takeover protection, and more. It also offers a virtual terminal that allows a business to accept payment from any device.
2. Payoneer

Payoneer is an American online payment service provider that enables businesses to send and receive payments. It facilitates international payments by leveraging its presence in 200+ countries with 150 local currencies worldwide.
The payment gateway lets merchants accept payment in the customer’s local currency and converts it into a currency that they want. Payoneer facilitates faster payments; it delivers payments in as fast as 2 hours.
Payoneer offers the end customer a Payoneer account to manage their payments. Furthermore, Payoneer offers a system by which one can directly withdraw funds with a debit card. Some of the payment gateway’s services include cross-border payments, working capital, risk management, and tax solutions.
Payoneer allows you to connect with partner ecosystems opening up multiple opportunities to connect and expand your business. From small to large businesses, especially the ones operating internationally use Payoneer for online transactions as its fees are lower than PayPal.
3. PayCafe

PayCafe is an all-in-one payment service provider that caters to businesses of all sizes. They offer services for one-time payments, subscriptions, or invoices.
Once the initial setup process with the marketplace has been completed, it can accept payments. There is no need to combine the PayCafe payment gateway with any other system or vendor.
PayCafe offers services such as Currency Conversion, Payment risks management, and Customized Emails. Additionally, PayCafe also offers 24X7 customer support via phone. The payment gateway comes with analytics tools and a fraud protection system.
4. Helcim

Helcim is a payments company that offers faster, smarter, and more affordable payments to businesses in Canada and the US. All Helcim accounts include access to the Helcim Merchant Platform that gives businesses access to tools that make it easier to get paid, including a virtual terminal, online store, invoicing, payment pages, and more.
Businesses with Helcim can accept all major credit and debit cards or request bank payments from customers. The Helcim API gives businesses the flexibility to integrate payments and provide customizable and flexible solutions for different business needs.
Business owners can use the Helcim API to interact with their existing Helcim account or as a traditional payment gateway API on their websites to process online payments.
More importantly, with Helcim, developers can perform more than 80 different API actions easily. For example, your developer can integrate your website, shopping cart, billing system, or application directly with our payment platform.
You should know that Helcim allows you to process online transactions that include sales, recurring payments, pre-authorizations, voids, refunds, card-tokens, captures, and more.
5. Stripe

Stripe commenced operations in 2011. It is a unified platform that offers an integrated suite of payment products to send and receive payments. Stripe has customizable features. Businesses that have the capability of an in-house code team or plan to outsource this task can utilize the customizable development features. Stripe has multiple APIs that allow the creation of subscription services, integration with on-demand marketplaces, or crowdfunding platforms. These services allow businesses to accept payments via any of the methods mentioned above.
Stripe supports multiple development languages, including Ruby, Python, PHP, and Java, giving the developers enough flexibility and ensuring integration with multiple websites and software. Stripe has local acquiring in 35+ countries and supports payments in 135+ currencies, giving the business flexibility to operate internationally. It also offers services that enable payments to be handled 100% on your site.
6. PayPal (Standard Plan)

PayPal is a globally trusted brand that has been in business since 1998. It allows to send and receive payments in cash or even cryptocurrency (restricted to a few states within the US). PayPal is active in more than 200+ countries and supports 100+ currencies. It has a presence in about the same number of countries as Payoneer, but the supported currencies are lesser. It offers the merchants a one-stop shop that includes a POS, a merchant account, invoicing functionality, and the means to accept payments.
This online payment gateway provides a better customer experience to the buyers. It gets linked to the buyers’ bank accounts to facilitate direct payments. PayPal also lets the merchants lower recurring costs with lower transaction charges.
Related: Best PayPal Alternatives for International Payments (SMBs)
7. Google Pay

Google Pay is one of the cheapest payment service providers. It leverages the global penetration of Google and its services. Google pay sets itself apart by offering integration with other Google services.
For instance, users can do money transactions via Google’s email service, Gmail. Google pay offers easy integration and is easy to set up for businesses. It facilitates a faster checkout process and features enhanced security. Google is a trusted name world over, which means more buyer trust, resulting in higher sales.
Related: Best Shopify Alternatives (Free, Open Source & Paid)
Functioning of Payment Gateways:
Payment Gateways act as “middlemen” (or a channel) that takes the customer’s payment and transfers it to the merchant, all via a secure and encrypted process. APIs of payment gateways have to be integrated with the website. Simply put, Application Programming Interface or API is code that lets two software interact with each other, exchanging data.
The payment process discussed below has the following parties involved in the entire payment realization process.
- Acquiring bank is a bank that processes the payments of the credit or debit card. The merchant should have an account with this acquiring bank.
- Issuing bank is a bank that issues credit cards to people on behalf of card associations. The customer should have an account with this bank.
- Card Association is a network of banks or an organization that enables card transactions. For instance, Mastercard, Visa, AmericanExpress, and others. Some card associations issue credit cards independently while others, like Visa, partner with banks to issue the credit cards to the customer.
- Payment processor is the financial entity that actually handles the transaction between the issuing bank and the acquiring bank. The payment processor and the payment gateway can be a single entity. For instance, in the case of Stripe, Braintree and others.
- Payment Gateway, as discussed above, collects and authorizes the information from the eCommerce website and transfers it to the payment processor.
Payment Gateways Complete the Transaction via the Following Steps:
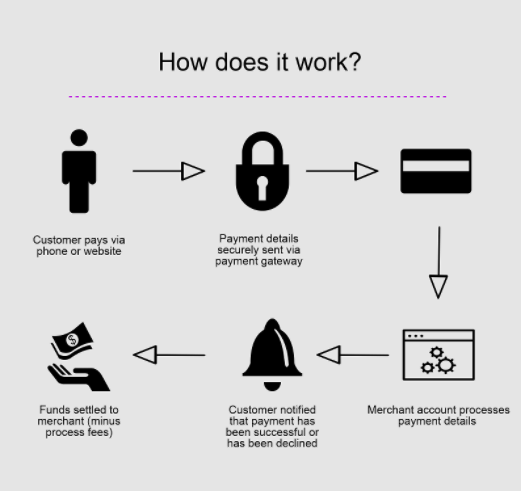
- A customer initiates a transaction by clicking on the button provided on the website. The customer fills in all necessary information regarding the payment method. An order ID is generated.
- Payment details of the customer are encrypted with a Secure Socket Layer or SSL. This encrypted data is sent from the browser to the merchant’s server.
- Merchant’s server forwards this encrypted data to their payment gateway.
- The data is now converted to an accepted format and transferred to the merchant’s acquiring bank account that will receive the payment.
- The merchant’s bank transfers this transaction data to the customer’s card authority.
- The card authority authorizes the transaction by reviewing the card details punched in by the customer.
- After successful verification of details, the merchant receives a message to fulfill the order.
- Funds are then transferred to the merchant’s bank account immediately or in a batch process.
Fraud Management in Payment Gateways:
A secure ecosystem is a key to the operations of Payment Gateways. They undertake many protocols to ensure cases of Fraud are minimized. Check some of these protocols listed below.
1. CVV and AVS
AVS stands for Address Verification System. This is associated with the customer’s card to help the card association verify the address of the customer the card is issued to. CVV is short for Card Verification Value, a three-digit number printed on the card itself. This number ensures that the person using the card has the card physically with them. The card issuing authority verifies these two numbers to ascertain the person’s identity using the card to make the purchase. In case of a fraud attempt first, the AVS is verified and CVV after that.
2. Device Identification
Every device has a unique number attached to it called the IP address of the device. Device Identification analyzes the IP address of the device that fraudsters are using. Apart from the IP address, it also considers the internet connection, the operating system, and the user’s browser. Any suspicious activity is flagged. Moreover, a database is maintained that lists and flags past offenders.
3. Payer Authentication
During the transaction, the buyer is asked to enter a unique pin provided via email or message during the transaction or predetermined by the user.
4. Lockout Mechanisms
Lockout mechanisms are emergency protocols that block a card after some repeated failed attempts at using the card.
Factors That Influence the Choice for Payment Gateway:
Although Payment gateways have been around for some time, businesses have many many payment gateways to choose from only in the recent few years. Finding the right payment gateway for the business will need research. We have laid down some parameters that can help you make a well-informed decision.
1. Buyers’ Security
Securing the buyers’ peace of mind can be one of the top priorities while choosing the right payment gateway for your business.
The payment gateway service provider should be compliant with the Payment Card Industry PCI Data Security Standards DSS. The PCI DSS is a set of requirements that ensure that all protocols are met for a secure transaction. This compliance is the verification of a secure payment gateway.
2. Flexibility of Payment Gateways
The only constant in eCommerce is changing. So whether the business scales up or there is a change in the business model. A flexible payment gateway would adapt to the changes in the e-business.
3. Costs of Payment Gateways
There are many ways payment gateways charge for the services they offer. To start with, a business will have to consider three modes in which payment gateways charge signup fees, monthly fees, or transaction fees. For a startup, every infrastructural cost adds up and takes away part of the working capital. Some payment gateways do not levy any signup charges; this might be an important consideration for such businesses.
Apart from the signup charge, there is a periodic service fee that payment gateways entail. Additionally, the payment gateway may levy a fee for each transaction. The transaction fee is always a percentage of the total transaction.
Apart from these changes, there are many other non-recurring costs associated with payment gateway services. There may be chargeback fees, PCI DSS compliance fees, early termination charges, and others. There are charges which are specific to particular payment gateways. For instance, Payoneer has a host of charges for its international transactions. Stripe charges a radar fee and so on.
It is important to discern between all types of costs applicable and be clear about the total cost the business will have to bear for the payment gateway.
4. Support for Multiple Currencies
If the business intends to operate in more than one country, support for multiple currencies is essential. Such payment gateways make it possible for a business to charge the buyer in the native currency. This is a crucial factor for the success of the business.
5. Performance
Paying for the product is the last step in the buyer’s journey. This step needs to be as fast as possible, both for the buyer and the business. This ensures maximum sales conversions. So the speed at which the payment gateway processes the transaction is an important factor.
Similarly, failed transactions may disappoint the buyer and, worse still, might let second thoughts creep in the buying decision. So, a payment gateway needs to have a high success rate. Additional consideration could be making sure that the payment gateway does not warrant an additional login process during the payment process. For the reasons discussed above, undesirable performance might negatively impact sales for the business.
6. Customer Support
eCommerce stores have successfully leveraged the convenience of shopping anywhere and anytime to the buyer. This also means that the buyers may need customer support 24X7. Since the payment gateway becomes a part of the eCommerce business, customer service will have to be at par with e-business offers.
7. Terms and Conditions
The terms and conditions of payment gateways vary, and it is an important consideration for a startup. For instance, some payment gateways have exceptions for the products and services they provide services for. It is just one of the reasons why terms and conditions of payment gateways should be part of planning for a startup.
Related: What Businesses are in High Demand Right Now?
8. Integrations and Setup
Seamless integration of payment gateways into the eCommerce software needs the expertise of a company well versed in eCommerce website development. A startup business will have to partner with an eCommerce website development company that has worked on eCommerce software.
Moreover, some payment gateways also offer integration with other systems within the eCommerce software like accounting software, invoicing software, and others. It smoothens the workflow of the eCommerce business.
The setup process of payment gateways differs too. For instance, some payment gateways like Authorize.net require a business to have a merchant account, while some like PayPal, Stripe don’t require a merchant account.
Hope, this comprehensive list of factors will help you decide the right payment gateway for your business. Based on these factors, we have listed the top payment gateways.
Umang is an accomplished digital marketer with a track record of success in SEO, ORM, and email marketing. He is enthusiastic about the SEO industry and is constantly eager to learn about the current search engine trends. Umang uses his abilities and experience to assist businesses in connecting with their target market.





















