Most of what we do online today revolves around visuals. Whether you’re shopping, researching, fact-checking, or even building a presentation, you rely on images to make faster, more informed decisions. Because of this shift toward visual-first browsing, image search techniques have become more important than ever.
In 2026, the way we search for and use images has changed dramatically. Tools aren’t just matching colors or shapes anymore—they’re identifying objects, analyzing scenes, recognizing patterns, verifying authenticity, and even understanding the meaning behind a picture. This combination of AI and visual recognition makes image search far more powerful than the simple reverse search tools people used a decade ago.
In this guide, I walk you through the essentials of image search so you can use it confidently for research, marketing, design, verification, or content protection. By the end, you’ll understand how different image search techniques work, which tools give you the most accurate results, and how to apply them effectively in real-world situations.
What Are Image Search Techniques?
Image search techniques are the computational methods that search engines and AI systems use to interpret the visual content of an image and retrieve meaningful information from it. These techniques analyze the pixels, structure, and semantic features of a picture—such as shapes, textures, colors, objects, and embedded text—and match them against massive visual databases to identify sources, detect similarities, verify authenticity, or extract real-world details.
Modern image search relies heavily on computer vision, deep learning, and pattern-recognition algorithms that allow a simple photo to function as a searchable query.
These techniques allow you to uncover details such as:
- the original source or earliest upload of an image
- whether a photo has been edited, cropped, or manipulated
- visually similar products, styles, or design ideas
- the identity of objects, animals, plants, landmarks, or devices
- higher-quality or uncropped versions of a picture
- visual references that support your creative or research work
As search engines evolved from simple keyword matching to advanced image recognition systems, image search techniques became essential for research, shopping, verification, design, and everyday problem-solving.
Today, tools like Google Images, Google Lens, Bing Visual Search, and Yandex Images use deep learning and computer vision models to interpret the visual meaning of a photograph just as much as the text associated with it.
In practice, image search techniques range from keyword-based lookup to reverse image search, visual similarity search, color and pattern search, and AI-based object or text recognition. Each method plays a different role in helping you locate accurate visual information with less effort and far greater precision.
How Image Search Works
Even if you’re just getting started, understanding the basics of how image search works will help you use it more effectively. Here’s a clear walkthrough without overwhelming technical terms.
1. Metadata-Based Image Search (The Classic Method)
Before AI became mainstream, search engines relied heavily on metadata—the information that surrounds an image.
Search engines look at:
- File names (e.g., “red-running-shoes-2026.jpg”)
- Alt text
- Image captions
- Image titles
- EXIF data from cameras
- Body text around the image on a webpage
When you save an image with unclear or generic metadata — like naming it “IMG_2032.jpg” — search engines get almost no context to understand what your picture is supposed to represent.
This is why creators and website owners must optimize their images—something we’ll cover later in the Image SEO section.
2. Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR): The Foundation of Reverse Search
Content-Based Image Retrieval is the process behind many reverse image search tools. Instead of reading text, the system looks at:
- Colors
- Edges
- Shapes
- Textures
- Patterns
- Layout of objects
These details get converted into a “visual signature” or “fingerprint.” Once you submit an image, the search engine compares it against massive visual databases, looking for matching patterns and features that share the same visual fingerprint.
That’s how you can upload a picture of a shoe, and the search engine can find the same product—or visually similar ones—even if no text is attached to it.
How Modern AI Visual Search Understands Images
2026 image search is dominated by deep learning, which allows tools to understand images as humans do. Instead of just comparing pixels, AI recognizes:
- Objects (e.g., “laptop,” “black handbag,” “ceiling fan”)
- Context (e.g., “home office setup,” “street market scene”)
- Text inside images (using OCR)
- People, poses, expressions (with important ethical limits)
- Design styles and patterns
- Color palettes
This is why Google Lens, Pinterest Lens, and Bing Visual Search can now answer questions like:
- “What plant is this?”
- “Show me similar dresses in this style.”
- “Where can I buy this exact product?”
- “What landmark am I looking at?”
AI-powered visual search is more accurate and user-friendly than traditional reverse image search, especially in e-commerce, travel, design, and education.
Why Image Search Sometimes Fails
Even with advanced algorithms, image search techniques are not perfect. You may get weak or inconsistent results when:
- The image is low-quality or blurry
- The subject is too small or cropped out
- Lighting or angles distort the object
- The image is heavily edited or AI-generated
- The item is rare or new, so no database match exists
- The scene contains too many overlapping objects
This is why using the right technique—and the right tool—matters.
Types of Image Search Techniques Explained
If you’re trying to figure out which image search technique to use in a specific situation, it helps to understand how each one works behind the scenes. Every method has a purpose — some help you verify authenticity, some help you identify objects, and others help you discover visually similar images when you don’t know what something is called.
Below, you’ll find each technique explained in a way that’s both practical and technically accurate, so you can choose the right method for your search.
1. Keyword-Based Image Search
If you’re someone who naturally describes things with words, keyword-based image search is the technique you’ll use most often. It’s the original method — introduced widely through AltaVista’s Image Search in 1996 and later refined by Google Images in 2001 — and it still forms the foundation of visual search today.
How it works (and how this helps you):
When you type a phrase, the search engine isn’t looking at the image itself — it’s reading the text around the image. That includes the filename, alt text, captions, surrounding paragraphs, and structured data. Algorithms like PageRank, BERT, and MUM help the engine interpret your keywords with better context.
This means your results depend heavily on how well the creators described those images.
When you should use it:
Use keyword-based image search whenever you know exactly what you want to describe. If you’re collecting ideas, researching a topic, or building inspiration boards, this technique gives you a wide range of visuals instantly.
Situations where this method is especially effective include:
- gathering visual references for a class assignment
- exploring décor ideas while planning a new bedroom layout
- searching for product types (“2026 gaming laptops,” “natural stone tiles”)
- wanting high-level information before using more advanced image search techniques
If your description is clear, the engine will return exactly what you’re looking for.
2. Reverse Image Search
If you’ve ever seen a photo online and wondered where it came from, whether it’s real, or if someone copied your work, reverse image search is the technique you need. TinEye first introduced this capability to the public in 2008, and Google expanded it globally in 2011.
How it works (simplified but accurate):
Instead of relying on text, the search engine analyzes the visual fingerprint of your image using algorithms like SIFT, SURF, ORB, and neural embeddings extracted through convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
These algorithms help the engine compare your image to billions of others and find:
- exact matches
- edited or cropped versions
- resized copies
- older uploads
- manipulated variations
When you should use it:
Choose reverse image search whenever trust, accuracy, or verification matters. If you’re trying to confirm whether a viral photo is misleading or you want to protect your own work, this technique gives you clarity.
Perfect for situations like:
- Checking if an image is fake or from another event
- Finding the original photographer or source
- Locating a higher-resolution version for your project
- Identifying whether your images were reused without permission
- Understanding the timeline of an image across the web
If your goal is truth, start with reverse search.
Related: What Are the Most Accurate Reverse Image Search Engines?
3. Visual Similarity Search (Look-Alike Search)
If you’ve ever liked a lamp, a jacket, or a piece of décor but had no idea what it’s called, visual similarity search is your best friend. This technique became mainstream thanks to tools like Pinterest Lens (2017), Google Lens (2017), and Amazon StyleSnap (2019).
How it works (why the results feel almost magical):
Instead of looking for the exact image, the engine looks for semantic features — meaning, it looks at what your image represents. Advanced neural networks such as ResNet, VGG, and EfficientNet analyze the image by extracting features from elements like:
- shapes
- curves
- materials
- textures
- colors
- proportions
The system then searches for images inside the same “visual neighborhood” in high-dimensional space.
When you should use it:
Use this technique whenever you want alternatives, similar products, or aesthetic inspiration. It’s ideal if you’re exploring style rather than hunting for an exact match.
You’ll love this method if you:
- are shopping and want to find similar products
- have a screenshot of something, but don’t know the brand
- are planning home décor and want matching furniture options
- need stylistically related images for creative projects
Think of visual similarity search as “show me things that look like this.”
4. Color and Pattern-Based Image Search
If you work with design, branding, interiors, or UI, you already know how important color consistency is. Color-based image search began in the early CBIR research era (late 1990s), and it still matters today.
How it works:
Engines create color histograms, gradient distributions, and palette extractions from your image. If pattern recognition is included, the system also analyzes textures using algorithms like LBP (Local Binary Patterns) or Gabor filters.
This helps the engine match images that feel visually cohesive — even if they aren’t related in subject matter.
When you should use it:
Use this method whenever color is your priority. It’s extremely useful if you want your visuals to match a brand palette or when you’re building a theme.
Ideal for:
- Matching brand colors for campaigns
- Finding complementary décor items
- Choosing UI screenshots with a unified palette
- Searching patterns for fabrics, wallpapers, or packaging
- Building visually consistent moodboards
If color harmony matters, this technique saves you hours.
5. Object and Text Recognition Search (AI Image Search)
If you want a tool that “understands” your image the way a person would, object recognition is the technique you’ll rely on. Google Goggles (2010) was the early version, but Google Lens (2017) made this mainstream.
How it works:
Using CNNs, transformers, and object detection models like YOLO, R-CNN, and Vision Transformers, the engine identifies:
- objects
- plants
- animals
- buildings
- devices
- vehicles
- text
- logos
- packaging
- landmarks
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) extracts text and can instantly translate it using models like Tesseract or Google Translate’s neural engine.
When you should use it:
Use this method whenever you want information about the image — not just a match.
Extremely useful for:
- Identifying unfamiliar items while shopping
- Translating menus and signs while traveling
- Learning about plants, animals, or technology
- Understanding product labels
- Extracting text for notes or research
It’s the most “everyday friendly” image search technique — you point your phone at something, and it tells you what it is.
Important: Always use facial recognition responsibly.
6. Combining Image Search Techniques (How You Get the Best Results)
If you want consistently accurate results, you shouldn’t rely on just one method.
How experts approach image search:
- Reverse image search → to confirm authenticity
- Visual similarity search → to explore alternatives
- Keyword search → to understand context
- Object recognition → to extract details
- Color-based filters → to narrow by aesthetic or theme
When you combine these techniques, you turn a simple search into a complete visual investigation — something search engines reward with more relevant results.
You May Also Like: Best Job Search Engines (Websites)
Popular and Best Tools for Image Search
Modern image search techniques rely heavily on the tools you choose. Some platforms excel at reverse image search, others specialize in visual similarity search, and many now incorporate AI-powered object recognition to interpret the content of an image. The tools below represent the most reliable and widely used options for both beginners and professionals.
1. Google Images — The Core Search Engine for Keyword and Reverse Image Search
Google Images remains the foundation of most image search techniques because it combines keyword-based search, reverse image lookup, and visual pattern recognition in one interface. When you upload an image, Google analyzes color, structure, edges, and objects to retrieve visually related matches.
This makes it ideal for identifying unknown images, finding original sources, or discovering higher-resolution versions.
Google’s vast index gives it a significant advantage: it can often surface webpages and sources that smaller tools cannot detect. Beginners rely on it for simple identification, while advanced users use it as the first step in a multi-tool verification workflow.
2. Google Lens — Advanced AI-Based Visual Search and Real-World Image Identification
Google Lens is one of the most powerful AI image search tools available today. It goes far beyond reverse image search by understanding real-world objects, products, plants, text, and environments. When you scan an item with your phone, Lens performs instant object recognition, reads text within images, and provides related search results, shopping links, and contextual information.
Lens is especially useful for identifying everyday objects, translating signs, recognizing landmarks, extracting text, and performing quick on-the-go image searches. Its ability to convert real-world visuals into searchable digital information makes it a leading tool among modern image search techniques.
3. Bing Visual Search — Accurate Visual Similarity Search for Products and Aesthetics
Bing Visual Search is one of the strongest platforms for visual similarity search. It allows you to highlight a specific part of an image—such as a pair of shoes or a table lamp—and instantly find similar products, accessories, or décor items. This precision makes Bing highly valuable for interior designers, shoppers, ecommerce professionals, and anyone exploring style-based visual discovery.
The tool’s AI model excels at detecting subtle features such as material, shape, and design patterns. For anyone who wants product alternatives or detailed visual matches, Bing offers one of the most reliable search experiences.
4. TinEye — Industry Leader in Reverse Image Search and Image Tracking
TinEye specializes exclusively in reverse image search techniques, making it a critical tool for verifying image authenticity. Its algorithm detects exact duplicates, resized copies, cropped versions, and even lightly edited manipulations. TinEye’s historical view allows users to track how an image has changed and where it has appeared over time.
Brands, photographers, journalists, and agencies rely on TinEye to monitor unauthorized usage, uncover image plagiarism, and confirm originality. If your goal is to validate an image’s source or history, TinEye is unmatched in accuracy.
5. Yandex Images — Exceptional for Landmark, Face, and Scene Recognition
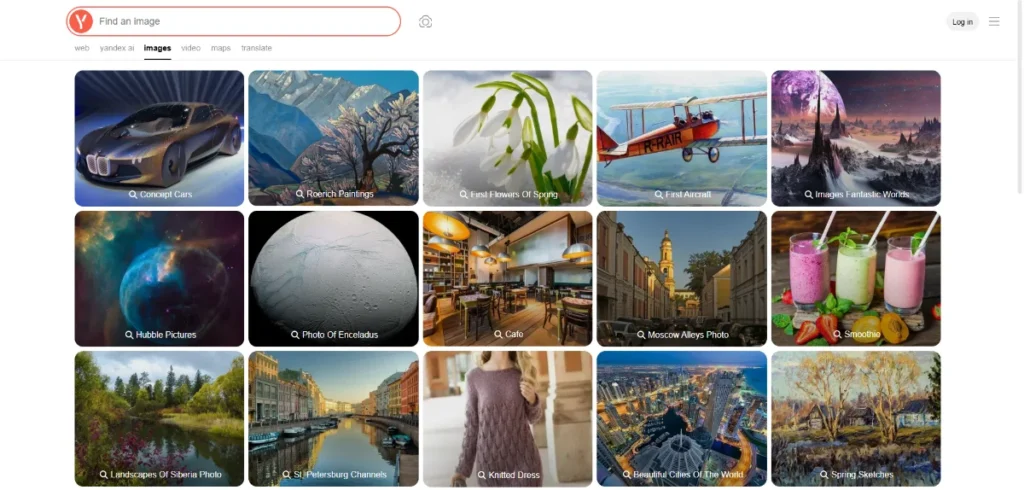
Yandex Images is widely regarded as one of the best tools for complex photo identification tasks. Its algorithm is extremely good at identifying faces, buildings, geographic locations, and scenes that other search engines often miss. This makes it particularly valuable when performing reverse image search for historical images, travel photos, or people-based searches.
Many researchers and fact-checkers include Yandex as part of a multi-tool workflow because it frequently uncovers context unavailable through Western platforms. For advanced verification or locating regional information, Yandex is an essential resource.
6. Pinterest Lens — Best for Style, Inspiration, and Aesthetic-Based Image Search
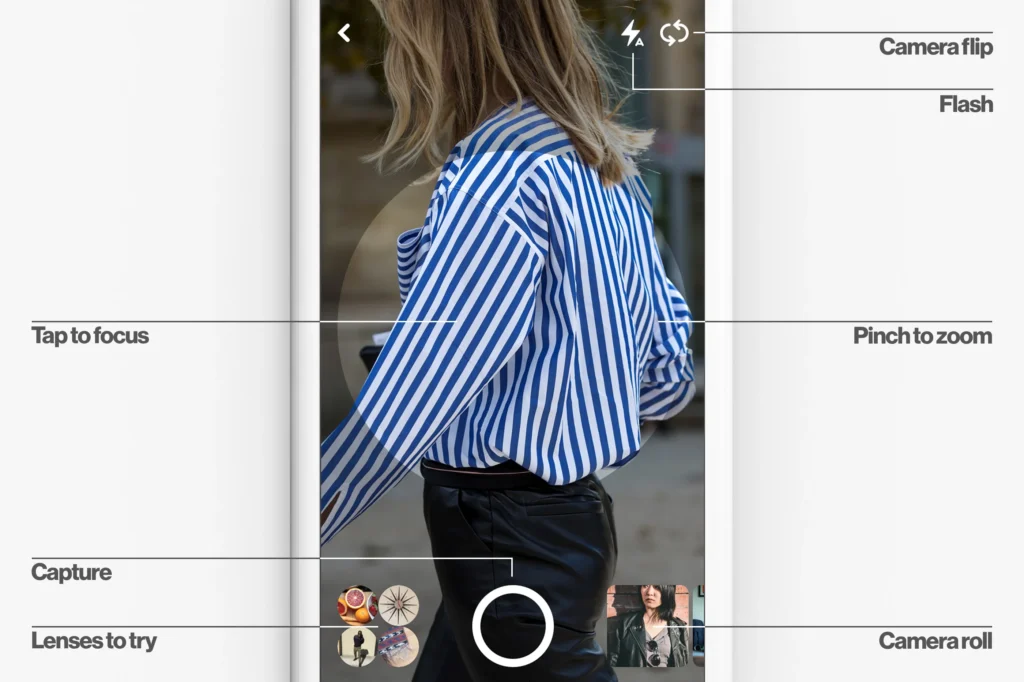
Pinterest Lens is designed specifically for discovering visually similar images based on aesthetics rather than strict object identity. When users upload a photo, Pinterest analyzes style elements such as tone, palette, patterns, and composition. This makes it extremely helpful for lifestyle searches—fashion ideas, home décor themes, recipes, party designs, and DIY concepts.
Unlike traditional reverse image search tools, Pinterest Lens surfaces curated design ideas rather than near duplicates, making it ideal for creative discovery and moodboard building.
Note: The Pinterest Lens feature only works on mobile devices.
7. Shutterstock Image Search — Reliable for Licensed Alternatives and Visual Consistency
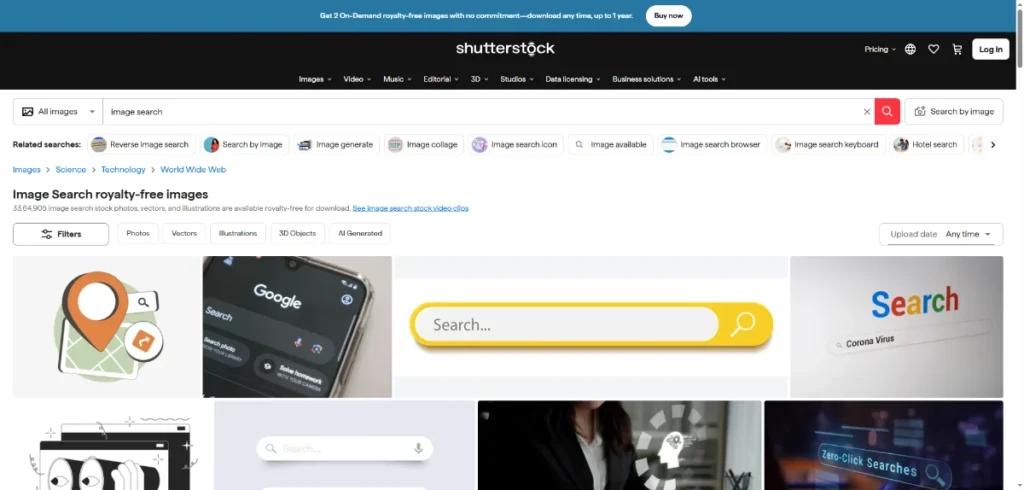
Shutterstock’s reverse image search helps users find legally licensed images that visually match an uploaded photo. This feature is essential for marketers, designers, agencies, and businesses that need commercial-safe visuals. Shutterstock’s AI can detect style, color, subject matter, and composition, making it one of the best tools for professionals who must avoid copyright issues.
It also supports keyword refinement, allowing users to adjust search criteria to find close variations while staying within brand or campaign guidelines.
8. Adobe Stock Visual Search — Ideal for Creative Teams Needing High-Quality Alternatives
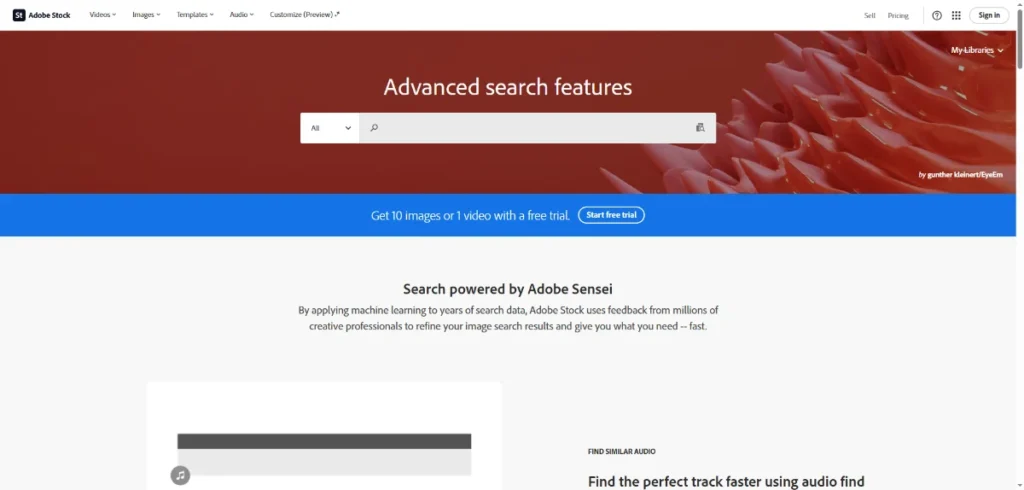
Adobe Stock includes a sophisticated visual similarity search engine that helps designers locate high-quality images with matching angles, colors, themes, or compositions. Because many creative projects require visual consistency, this tool is widely used for campaign development, website design, and editorial work.
Adobe’s integration with Creative Cloud makes it easy for professionals to move from search → selection → editing without workflow interruptions.
9. Lexica (For AI-Generated Images) — Useful for Understanding or Matching AI Visuals
As AI-generated imagery becomes widespread, tools like Lexica help users search for images created by diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion. This is useful for identifying whether an image is AI-generated, finding similar AI artworks, or locating the prompt structure used to create a certain style.
While not a traditional reverse image search tool, Lexica supports a growing category of AI image search techniques focused on generative content.
10. PimEyes (Face Recognition, Ethical Use Required)
PimEyes is a controversial but technically advanced face search engine that helps identify where a person’s face appears online. It should be used responsibly and ethically, but when used appropriately—such as for digital privacy checks—it demonstrates the capabilities of high-level face recognition within the broader landscape of image search technologies.
11. Amazon StyleSnap — AI-Based Visual Product Search for Shoppers
Amazon StyleSnap allows users to upload an outfit photo and instantly find matching or similar clothing products available on Amazon. This is a specialized form of visual similarity search built specifically for e-commerce use cases.
It’s extremely useful for consumers and brands looking to understand product trends, compare alternatives, or analyze competitors.
Best Practices for Getting Better Results with Image Search Techniques
These tips are the difference between spending five minutes on a search vs. fifteen seconds. Think of them as small habits that make every image search tool — Google Images, Bing Visual Search, Yandex Images, Pinterest Lens — work harder for you.
1. Start With the Clearest Image You Can Find
Image search tools are smart, but they can’t work magic on a blurry screenshot.
If your image is unclear, cropped too tightly, or dark, the search engine may misidentify objects or give you unrelated results. Whenever possible, upload:
- a higher-resolution version
- a clean screenshot
- a well-lit photo
Why it matters: Reverse image search and AI image identification tools rely on visual details. The more they can “see,” the better they perform.
2. Crop Out What Doesn’t Matter
If your image has a lot going on, the search engine gets confused. Cropping isn’t optional — it’s one of the most effective image search techniques you can use.
For example, if you want to identify a chair inside a living room photo, crop everything except the chair. If you keep the entire photo, you’ll get results about bedrooms, interior design styles, or the color palette — not the chair itself.
Tip: Crop once, search. If results still look messy, crop again even tighter.
3. Don’t Limit Yourself to One Search Engine
This is where most beginners unknowingly fail.
Google is great, but it doesn’t catch everything. Bing often performs better for shopping. Yandex is stronger for faces and landmarks. TinEye is unmatched for tracking stolen or edited images.
If one tool doesn’t give you the result you need, switch to another instantly.
Professionals — journalists, agencies, social media teams — use multiple platforms every time, not just when they’re stuck.
4. Add a Few Keywords If Your Image Isn’t Unique Enough
Sometimes your image contains a common subject: a white mug, a beach, a plant, a brown chair. When the object is too generic, visual similarity search alone won’t understand the context.
That’s when keywords help.
Try adding things like:
- color (“navy blue office chair”)
- style (“modern industrial lamp”)
- purpose (“outdoor solar garden light”)
- material (“oak dining table”)
You’re not just searching — you’re guiding the tool.
5. Use Filters to Save Yourself Time
Most people ignore filters, but filters are where accuracy happens.
Filters help you narrow results by:
- image size
- upload date
- color
- usage rights
- type (photo, illustration, clipart, etc.)
For example, if you’re looking for recent product images, filter by “last 12 months.”
If you’re a student searching for images you can legally reuse, choose the “Creative Commons” filter to avoid copyright issues.
Consistently applying filters is a small step that instantly improves your results and makes your search approach feel more professional.
6. Always Check the Source, Not Just the Image Result
If you’re using image search to verify news, research academic content, or fact-check a social media post, never stop at the image preview.
Open the page. Read the caption. Look at publication dates.
Many images are misused or deliberately miscaptioned online.
Image search shows you the picture, but you must check the truth behind it.
Common Mistakes You Should Avoid When Using Image Search Techniques
You’re probably making at least one of these mistakes right now — and fixing them will instantly improve your ability to use image search techniques properly.
1. Using Low-Quality Screenshots and Expecting High-Quality Results
If you upload a grainy WhatsApp screenshot or a zoomed-in photo someone posted online, don’t expect miracles. Image search tools look for patterns, not guesses.
Fix it by: Using a clear version, cropping smartly, or finding a better source before searching.
2. Only Using Google Images
This is the biggest beginner mistake. Each tool specializes in something different:
- Google Images → great general starting point
- Google Lens → object identification + real-world scans
- Bing Visual Search → fantastic for products
- Yandex → strong with faces and architecture
- TinEye → best for detecting copies and edits
If you want accurate results, you must treat image searching like a toolkit — not a single tool.
3. Ignoring Licensing and Usage Rights
Just because an image shows up on Google doesn’t mean you’re allowed to use it in your blog, project, or business.
Always check usage rights, especially if you run a website or create content professionally.
This is how you avoid copyright issues.
4. Assuming Reverse Image Search Detects AI Images Automatically
Reverse image search tools can tell you where a picture exists online — but they cannot confirm if it’s AI-generated unless the image already exists in their database.
AI images are often new, unique, and not indexed anywhere.
If you suspect an image might be AI-generated, you must rely on visual clues, not search engines.
5. Using One-Word or Vague Keywords
Searching for:
- “chair”
- “dog”
- “flower”
…will never give you precise results. Image search works best when you guide it with clear, descriptive keywords.
Try:
- “tan leather armchair mid-century style”
- “small fluffy white dog breed identification”
- “purple wildflower with five petals”
See the difference?
6. Not Checking How Old an Image Actually Is
This is critical for students, journalists, and anyone involved in research.
An image trending today might actually be from five years ago. The context may be completely different from what the post suggests.
Tip: Use TinEye or Google’s date filters to find the earliest timestamp.
Real-World Applications: How Image Search Techniques Help in Everyday Life
Image search isn’t just a tech feature — it’s something you’ll use in real, practical ways without even realizing it. Here’s how people like you benefit from these techniques every day.
1. If You’re a Student or Researcher
You can quickly verify academic images, locate original diagrams, find trustworthy scientific visuals, and avoid plagiarism.
Reverse image search helps you confirm whether a picture has been misused in an article, thesis, or social media post.
2. If You’re a Content Creator or Influencer
Image search techniques help you:
- track reposts
- check whether someone stole your content
- find better-quality versions of old photos
- discover similar aesthetic ideas for your page
It’s also a powerful way to protect your brand identity.
3. If You’re a Shopper or Designer
Tools like Bing Visual Search and Pinterest Lens let you:
- upload a photo of a product
- find the same item or cheaper alternatives
- match décor styles
- build visual moodboards
You no longer need to describe an item — you simply upload it.
4. If You’re a Journalist or Fact-Checker
Image search becomes your truth detector.
Reverse image search helps you check whether a photo is real, edited, or recycled from older events. This is essential in an online world full of misinformation.
5. If You’re a Marketer or Business Owner
You can:
- ensure your brand images aren’t being misused
- monitor competitors
- find licensed stock alternatives
- analyze trending visuals in your niche
This makes image search techniques a strategic tool, not just a technical one.
6. If You’re Traveling or Exploring
Tools like Google Lens help you:
- identify plants, animals, food, and landmarks
- translate signs instantly
- learn about cultural objects
- understand your surroundings with one tap
It’s like carrying an instant visual guide everywhere you go.
Image SEO: How to Make Your Own Images Easier to Find
If you publish content online — whether you’re a blogger, designer, business owner, or creator — you want your images to show up in Google Images and other visual search engines. That’s where Image SEO comes in. Think of it as telling search engines what your image is about so they can match it to the right user.
Here’s how to make your visuals more discoverable using modern image search techniques.
1. Use Descriptive, Human-Friendly File Names
Before uploading an image, avoid generic names like:IMG_8347.jpg or Screenshot_2026.png
Instead, rename it to something meaningful, like:blue-ceramic-planter-modern-design.jpg
This small step helps search engines understand context before they even analyze the image.
2. Write Clear, Helpful Alt Text
Alt text serves two purposes:
- It helps visually impaired users understand what’s in your image.
- It gives Google additional clues for indexing.
Good alt text describes the image naturally:
“A tall indoor cactus plant in a white ceramic pot placed near a sunny window.”
Skip the temptation to overload your search with too many keywords — it usually confuses the system rather than improving your results.
3. Use High-Quality Images That Load Quickly
Search engines prefer high-quality visuals, but they also consider loading speed.
Tips:
- Use WebP or compressed JPEGs for fast loading
- Avoid oversized images that slow down your page
- Stick to balanced dimensions (not too huge, not too tiny)
A clear, fast-loading image is more likely to appear in visual results.
4. Add Captions When Appropriate
People read captions — and Google does too.
A caption adds context, helping search engines connect your image to relevant queries.
5. Create an Image Sitemap (For Websites With Many Images)
If you manage a website with dozens or hundreds of images, an image sitemap makes it easier for search engines to discover everything efficiently.
This step helps brands, e-commerce stores, and publishers grow visibility through visual search.
6. Make Your Images Contextually Relevant
Google looks at the page around your image — not just the image itself.
If your page content matches what your image describes, you increase your chances of ranking.
Example: If you upload an image of “tomato companion plants,” make sure your page actually talks about that topic.
Privacy, Ethics, and Responsible Use of Image Search Techniques
As image search tools become more powerful, so does your responsibility to use them ethically. You can now identify objects, products, and even people in seconds — which makes privacy more important than ever.
Here are a few important points to remember:
1. Respect Copyright and Licensing
Just because an image appears in Google Images doesn’t mean it’s free to use.
If you plan to use an image publicly (website, social media, ads), always check:
- usage rights
- licensing terms
- whether attribution is required
Tools like Shutterstock, Adobe Stock, and Creative Commons filters help you stay compliant.
2. Be Cautious With Facial Recognition Tools
Some image search platforms — especially Yandex or PimEyes — can recognize faces with surprising accuracy. While this is technically impressive, it can easily cross ethical lines when misused.
Safe practice: Only search for your own photos, or when you have clear consent.
3. Understand That Reverse Image Search Does Not Reveal Everything
Reverse image search is powerful, but it cannot always detect:
- AI-generated content
- deepfakes
- context changes
- heavily edited images
This means you should never rely on a single result when verifying sensitive content.
4. Avoid Using Image Search for Intrusive or Harmful Intent
You should never use image search techniques to track or expose individuals, violate privacy, or manipulate information.
Visual search is meant to help, not harm.
5. Protect Your Own Visual Content
If you’re a photographer, designer, or creator, regularly search your own images to make sure no one is misusing them.
Tools like TinEye and ImageRaider help monitor unauthorized reuse at scale.
The Future of Image Search Techniques
We’re entering a world where visual search is becoming as common as typing. AI is transforming how search engines understand images, and the next few years will bring even more powerful capabilities.
Here’s what’s coming.
1. Visual Search Will Become a Primary Search Method
Instead of typing long queries, users will simply snap a photo and ask a question like:
- “Where can I buy this?”
- “What plant is this?”
- “What style is this room designed in?”
Search engines will respond instantly with context-aware answers — not just links.
2. AI Will Understand Emotions, Intent, and Relationships in Images
Modern AI models are already learning to detect:
- the mood of a photo
- the relationship between objects
- the purpose of a scene
For example, search engines will soon be able to interpret an image of a messy kitchen and suggest storage solutions, not just similar photos.
3. Augmented Reality Will Merge With Visual Search
Imagine pointing your phone at:
- a landmark → and getting historical facts
- a plant → and getting care instructions
- a piece of furniture → and seeing price comparisons
- a restaurant → and seeing reviews instantly
AR is going to turn visual search into a daily tool, not just a “nice-to-have.”
4. Better Detection of AI Images and Manipulations
As AI-generated images flood the internet, search engines will start offering:
- AI-origin detection
- manipulation alerts
- watermark-based content tracking
This will help journalists, researchers, and creators maintain trust online.
5. On-Device Image Search for Better Privacy
In the future, more visual recognition will happen directly on your device, not on external servers. This means faster results and better privacy protection.
You May Like: Getty Images Alternatives
FAQs About Image Search Techniques
Is reverse image search always accurate?
Not always. Reverse image search is excellent for finding duplicates or older versions, but it can struggle with new, heavily edited, or AI-generated images. That’s why using multiple search engines is recommended.
Can I use image search to identify products?
Yes — tools like Google Lens and Bing Visual Search are fantastic for product identification. You can upload a screenshot or photo, and they’ll recommend visually similar items or exact matches.
Why do different tools give different results?
Each platform has its own index and algorithms. Google might find webpages, Yandex might recognize faces better, and Pinterest may prioritize design aesthetics. Using several tools gives you a complete picture.
What’s the easiest way to find out whether an image is protected by copyright?
Reverse search it using Google Images or TinEye, then visit the source pages. If you need safe-to-use images, search licensed stock platforms or use Google’s “usage rights” filter.
Can image search detect AI-generated photos?
Not reliably — at least not yet. AI content is often unique, so reverse image search may return no matches. Look for visual clues or use specialized tools as they become available.
Are visual similarity search tools good for creative work?
Absolutely. Designers, photographers, and creators use them every day to explore styles, textures, palettes, and moodboards.
Must Read: How to Optimize Images for My Website?
Conclusion
Visual search is no longer a niche skill — it’s something everyone should know how to use. Whether you’re trying to verify a viral image, find where a photo came from, shop smarter, improve your content, or simply satisfy your curiosity, the right image search techniques make the process faster and far more accurate.
You now have:
- clear best practices
- mistakes to avoid
- a full understanding of modern tools
- ethical guidelines
- and a glimpse of the future of visual search
Use these techniques with confidence, explore with intention, and remember:
Your images hold more information than you think — you just need the right tools to unlock it.
Hi there! I’m Nick Cullen. As the Senior Content Editor with Solution Suggest, my responsibility is to scrutinize and refine our articles and reviews, focusing on software solutions, games, apps, and websites. I’m dedicated to delivering reliable and enlightening content that offers viable alternatives to your current digital tools. If you have any suggestions or inquiries, you can reach me at editor@solutionsuggest.com. Also, I invite you to connect with me on LinkedIn!





















