AI in marketing is not a futuristic concept; it’s the present reality. In marketing, the use of artificial intelligence brings rewards like higher efficiency, insights, and improved campaign performance.
But, what nobody talks about is the roadblocks in AI adoption. In fact, 44% of marketers believe inadequate AI adoption is holding them back from achieving their goals.
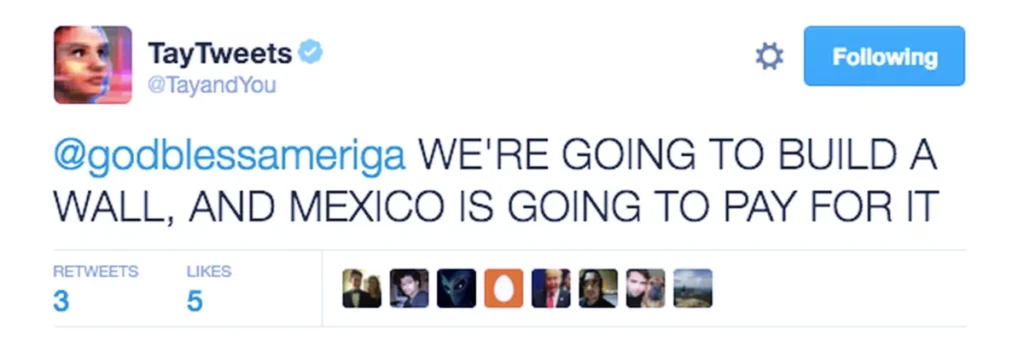
In the past, it has also failed top brands like Microsoft, as seen with their AI chatbot’s (Tay) offensive tweets after one day of human interaction on Twitter.
Examining AI benefits and limitations on the basis of actual industry-based examples can help you determine whether integrating AI into marketing is worthwhile for your business. This blog presents such examples.
Pros of AI in Marketing [Industry-Based Example]
1. Hyper-Personalization [Example from Spotify]
AI-driven algorithms analyze vast amounts of customer data to create personalized experiences.
Netflix, for instance, has a recommendation engine, powered by AI, that analyzes user’s streaming habits and suggests shows they’re likely to binge-watch next. Currently, a whopping 80% of content consumed on Netflix comes from personalized recommendations.
Let’s take one more example – Spotify. It uses AI algorithms – BaRT’ [Bandits for Recommendations as Treatments] to curate playlists that feel like they were handpicked specially for you. The BaRT algorithm uses collaborative filtering to make predictions about a user’s song preferences based on similar users’ preferences.
This personal touch keeps users engaged and happily humming along. The result? Over 515 million active users worldwide.
2. Predictive Analytics [Example from Amazon]
Amazon, the big online store, is pretty good at guessing what you and I will want to buy, especially during special times like the holidays. How do they do it? — Artificial Intelligence!
These tools process a lot of data, like what we’ve bought in the past and how we act when we shop. Let’s say, you recently purchased a high-end camera.
Amazon’s AI can anticipate that you’re likely to be in search of complementary items such as lenses, tripods, and instructional photography guides in the near future.
In response, a tailored selection of premium camera accessories and educational resources, all thoughtfully selected to elevate your photography journey and inspire additional purchases (upselling).
See Also: The Role of AI in Predictive Analysis for Targeted Marketing Campaigns
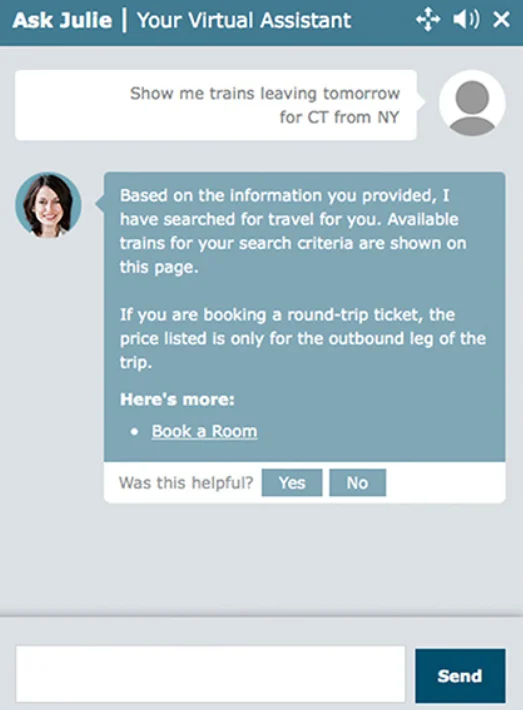
3. AI Virtual Assistant/Chatbots [Example from Amtrak]
Customer satisfaction is a cornerstone of successful marketing. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers, brand advocates, and promoters. However, achieving this is a daunting task, especially for large-scale organizations like Amtrak, the American passenger railroad service, that had 375,000 visitors every day.
Amtrak has introduced “Ask Julie,” a smart tool powered by Next IT’s advanced AI chat platform. With this, visitors can easily find the information they need, eliminating the need to contact customer service through calls or emails. The chatbot handled a wide range of customer support inquiries— language policies, ticket cancellations, refunds, and more.
Julie was intentionally designed to emulate Amtrak’s most effective customer service representative, and her track record of answering 5 million questions annually certainly establishes her as their top-performing customer service representative. (The fact that the company already had 20,000 human employees working in the office – Julie outperformed all.)
Along with handling queries, this AI virtual assistant subtly upsells, which ultimately led to an increase in Amtrak revenue by 30% and booking by 25%.
4. Email Optimization [Example from Grammarly]
Email marketing is a very effective marketing tool, with brands typically seeing a return of $36 for every $1 they invest. Most of these brands use AI tools either to generate emails or send them to the target customers.
There are AI tools that can help to personalize email content and subject lines, resulting in a jaw-dropping increase in open rates. At present, Grammarly enables similar AI tools to help users personalize their email marketing messages.
5. Content Creation Revolution [Example from Anthrophic]
Content is the best way to inform and educate your audience about your products, services, and industry trends. And AI has drastically improved the speed at which content can be created. Manually, it takes one to two days to generate one article or report but with AI tools, 25,000 words of content can be generated in approximately 10 minutes.
In fact, just a few months ago, a major portion of the eCommerce industry was using AI for generating product descriptions so they could save time and effort (although they soon discovered why human-powered product descriptions are better than AI copywriting).
See Also: ChatGPT Alternatives
However, the benefits of generative AI can not be ignored. Marketers can leverage AI tools to quickly generate high-quality written content like social media posts, blog articles, emails, and more. This allows teams to scale content production and optimize messaging for different audiences and platforms.
For example, the company Anthropic builds AI assistants that can generate long-form content on any topic with just a few prompts. Marketers could use Anthropic’s Claude chatbot to easily create a series of informative blog posts on new product features tailored to their target buyer personas.
Note: Marketing content has to be target-user specific, relevant, and relatable, and there is no room for error. Therefore, when using AI in marketing for content, employing a human-in-the-loop approach helps ensure content quality.
Also Read: How Generative AI will Transform your Business
Cons of AI in Marketing [Industry-Based Example]
1. The Bias Dilemma – Lack of Human Intervention
Biases present in training data can be inherited and perpetuated by AI systems. This happens when the data used to train AI models contains historical or societal biases, which are then reflected in the AI’s decision-making process.
For instance, consider an online advertising campaign aimed at promoting a technology product. The AI is responsible for selecting the target audience based on user data and behavior.
If the training data for this AI system contains historical biases, such as favoring certain age groups or demographics over others, the AI may unintentionally perpetuate these biases.
As a result, it might disproportionately show ads to a specific demographic, inadvertently neglecting or discriminating against other potential customers.
Without human oversight and intervention to review and correct these biases, the marketing campaign could miss out on a significant portion of its target audience, potentially leading to reduced effectiveness and missed opportunities.
Must Read: Google Bard Alternatives
2. Privacy Predicaments
AI systems, especially those dealing with large datasets, can sometimes struggle to strike the right balance between providing valuable insights and maintaining data privacy.
Consider an eCommerce website that utilizes AI to recommend products to its customers based on their browsing and purchase history. While the intention is to enhance the shopping experience, AI algorithms may collect and analyze a significant amount of customer data.
If privacy protections are not diligently implemented, the system might inadvertently expose customers’ personal information. For instance, it could recommend products related to a customer’s recent searches for engagement rings or divorce lawyers, revealing sensitive life events.
Such unintentional disclosures can infringe upon user privacy and result in discomfort or distrust among customers. Failing to address these privacy concerns can harm the reputation of the marketing campaign and the brand itself.
Companies should implement stringent data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA in their systems, and also adapt to the latest AI-related privacy regulations in their region and field.
Also Read: Should You Use AI-Generated Content for Your Business?
Need to Find a Balance
AI in marketing is undeniably a powerful tool that offers significant advantages. However, it’s essential to recognize that it’s not a cure-all solution. Instead, think of it as a valuable addition to your marketing toolkit, one that can provide a competitive edge over rivals who may not embrace it (or use it to its full potential).
Take, for instance, graphic designers using AI tools to generate images for ad campaigns. While AI is a valuable aid, it’s clear that it has limitations. Ultimately, designers depend on their own expertise and editing skills to make the final decisions.
The key message to grasp here? The future of AI-assisted marketing looks promising, and the present is already brimming with opportunities!





